For mineral-rich Philippines, green metals rush is a balancing act

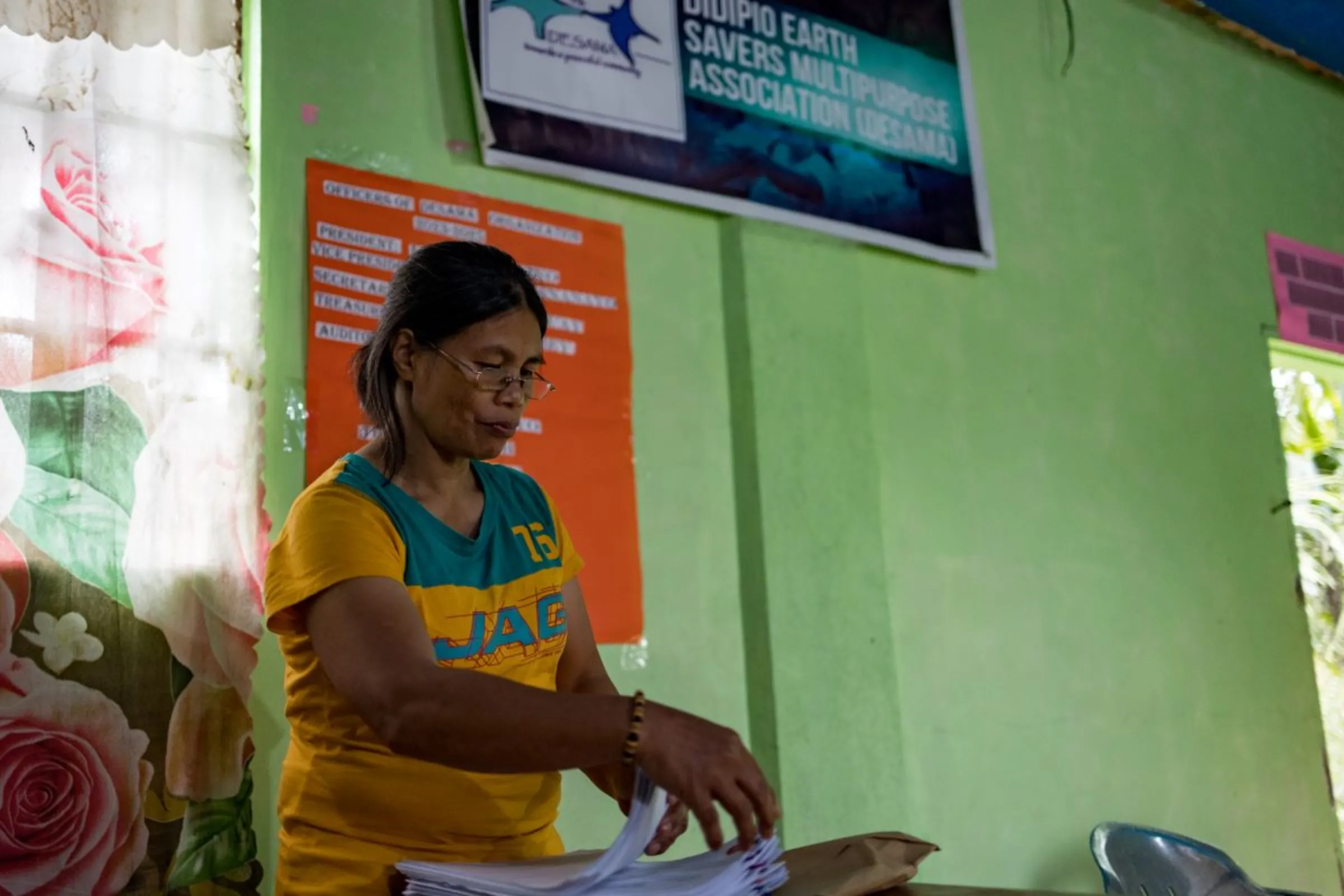
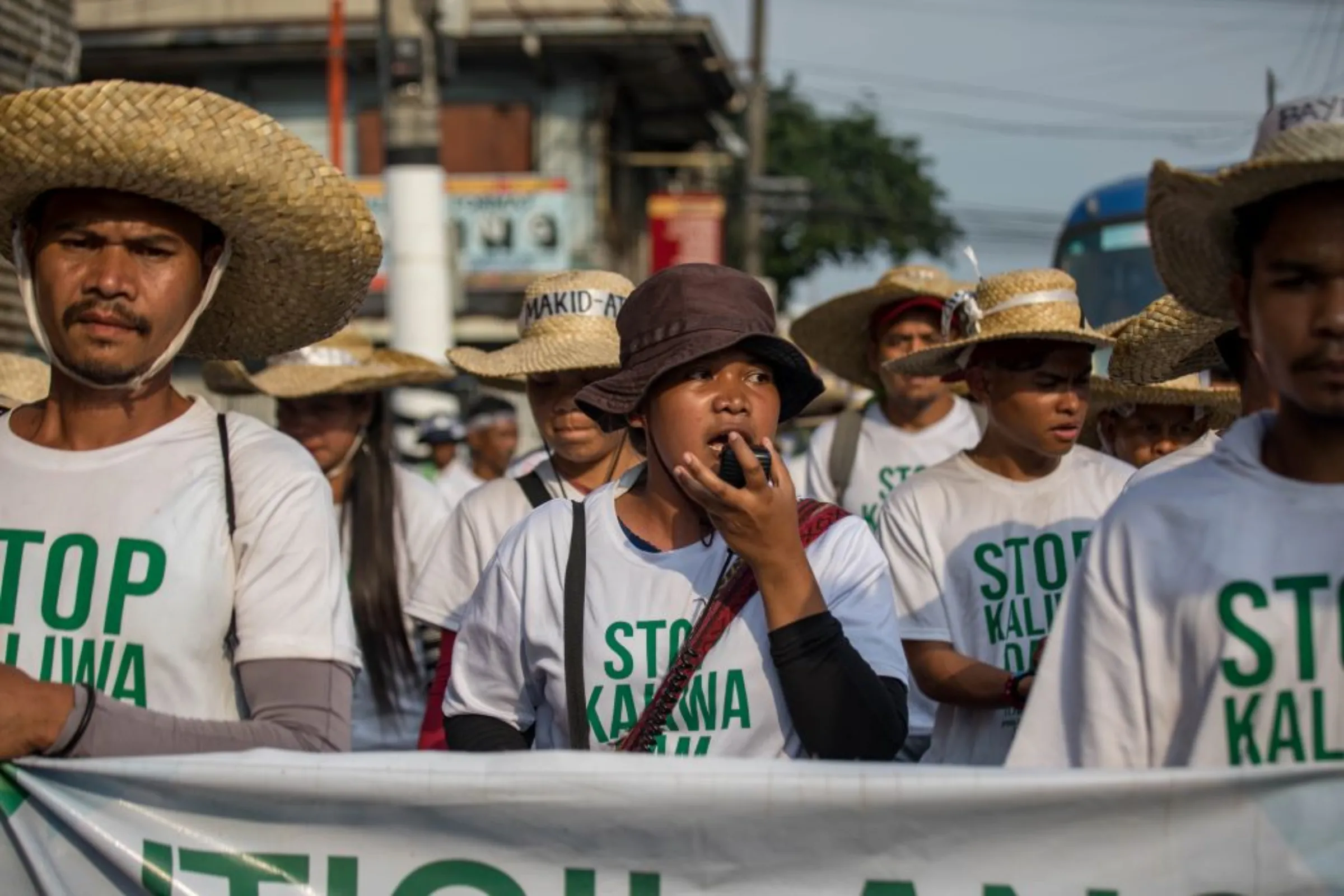
Anti-mining slogans displayed at a store run by a community group pushing for the closure of a mine in Didipio, the Philippines. Thomson Reuters Foundation/ Kathleen Lei Limayo
What’s the context?
With demand for metals used in clean energy soaring, Filipino campaigners say mining laws must protect nature and Indigenous lands
- Clean energy technologies fuel demand for copper, nickel
- Philippines wants to boost output of 'critical minerals'
- Green, Indigenous campaigners push for new mining law
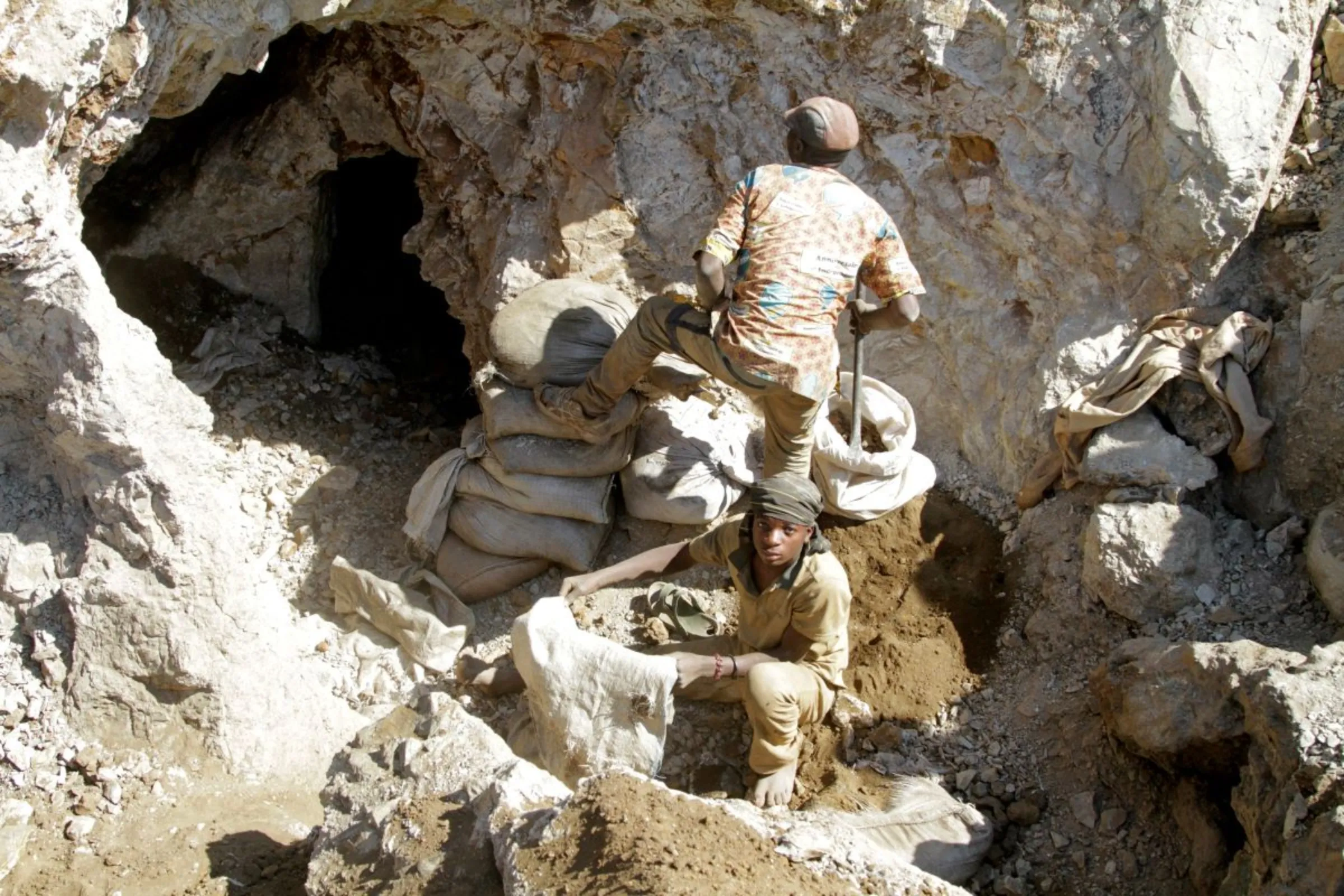
DIDIPIO, Philippines - As the Philippines works to ramp up mining to meet global demand for metals crucial to the green energy transition, environmental groups are demanding strict limits to protect nature and Indigenous lands.
The Philippines has the world's fourth-largest copper reserves, fifth-biggest nickel deposits and is also rich in cobalt - all of which have important uses in clean energy technologies, from lithium-ion batteries for electric vehicles (EVs) to solar panels.
Mineral requirements for renewable energy technologies must be quadrupled by 2040 to reach the goals of the Paris Agreement, and the World Bank estimates a 500% increase in the demand for transition minerals.
That is encouraging mineral-rich countries like the Philippines, where mining is relatively undeveloped and only accounts for 1% of gross domestic product (GDP), to boost their production of so-called critical minerals.
But with nearly two-thirds of the Philippines' mineral reserves lying on Indigenous lands, environmental and rights campaigners are demanding new legislation to limit mining activity to the minimum needed for the green energy switch.
"Mining is a necessary evil in our civilisation and daily life. But we believe in mining anchored on just minerals transition, or mining what is absolutely necessary and sourcing them responsibly," said Maya Quirino, advocacy coordinator at the Legal Rights and Natural Resources Centre (LRC), a local nonprofit that works for Indigenous and environmental rights.
"For example, gold is not essential to the energy transition," she told Context.
Quirino's organisation is leading calls for a new mining law that would only permit the "indispensable extraction" of critical minerals. It also seeks to prohibit destructive open-pit mining, or mining in sensitive ecosytems, and hike taxes on the companies to give great benefits to local communities.
A draft bill filed by lawmakers and supported by the LRC in 2021 is still pending in Congress, but its backers are working to gain more support this year from legislators.
Just transition?
Globally, the area covered by mines has doubled over the past three years, driven by demand for critical minerals, according to a 2023 study by LRC.
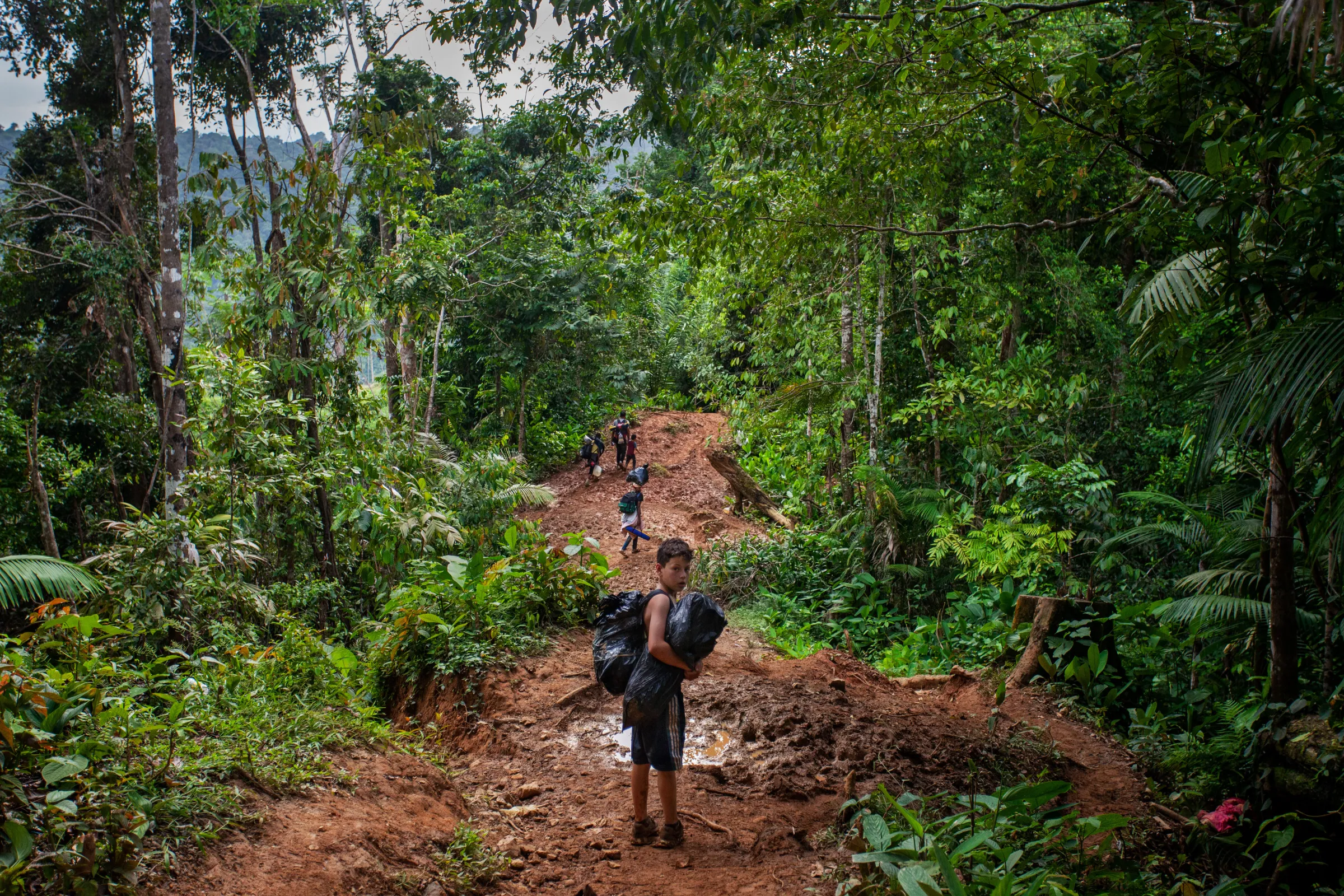
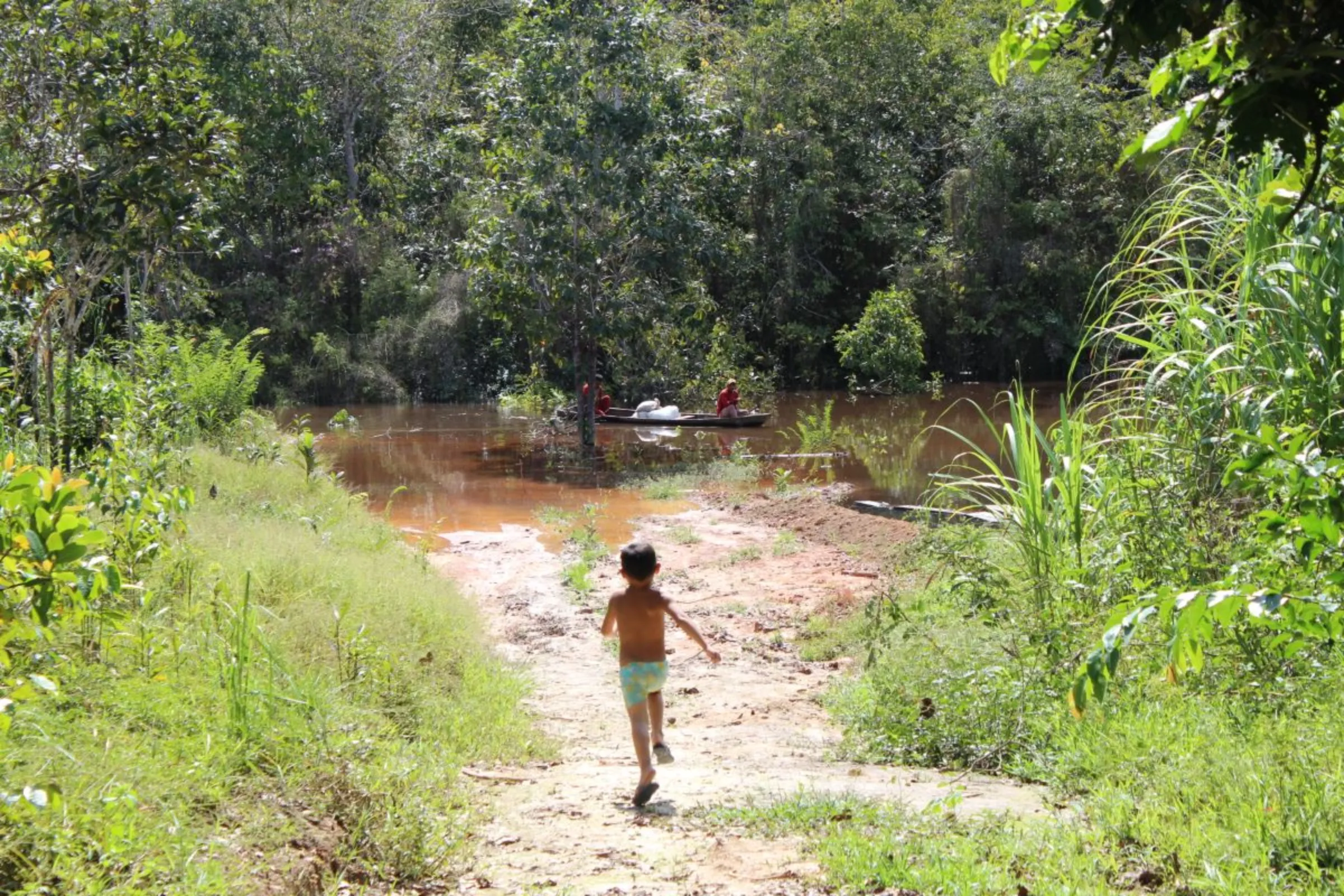
In the Philippines, the group says, that has exacerbated mining's negative impacts on people and the environment - whether by depleting water supplies or forcing Indigenous peoples to move elsewhere.
Mining projects in the Southeast Asian country have often prompted protests by Indigenous people and disputes over their land rights, and the impact of mines on the environment, including water supplies.
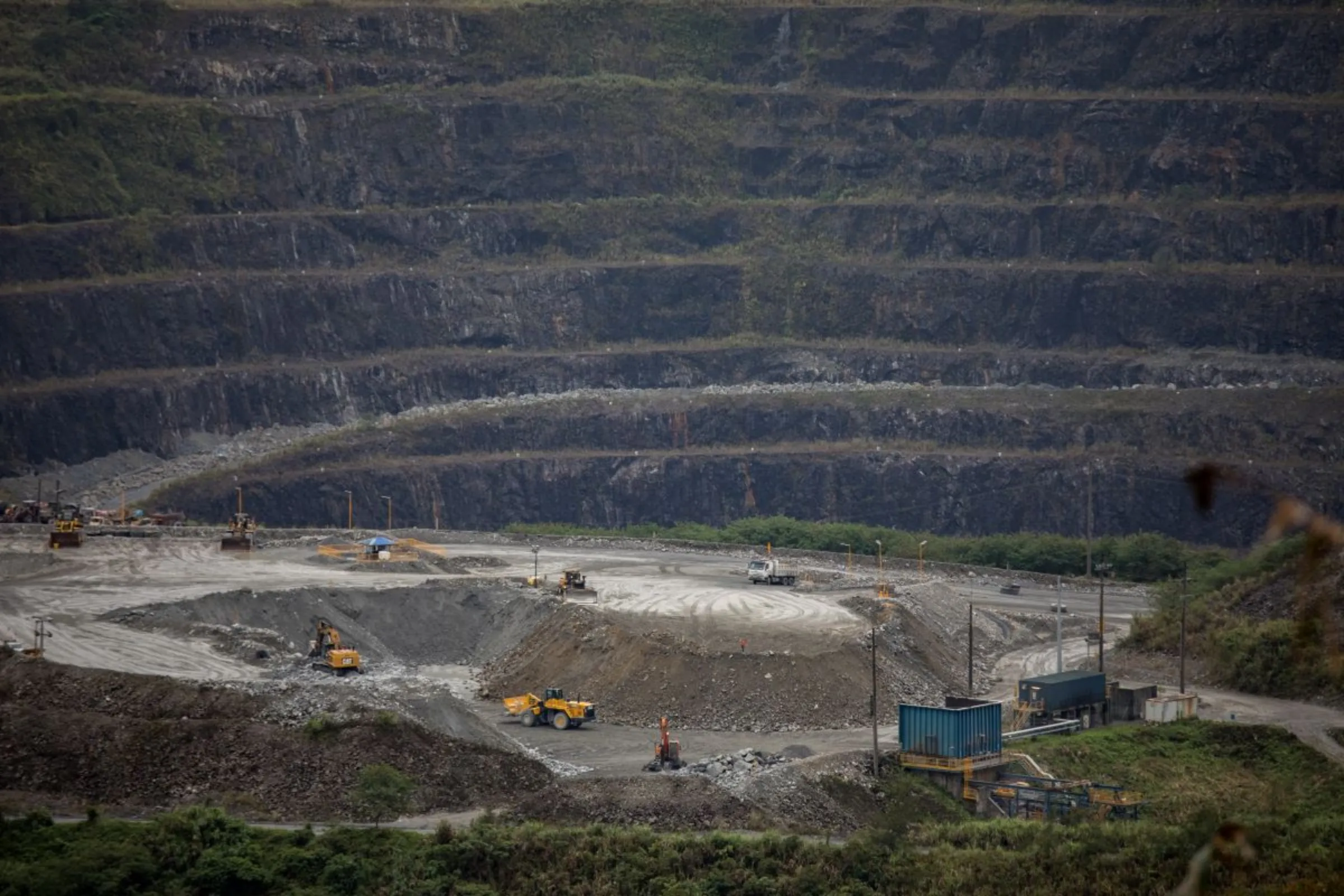
Recent examples include the Tampakan and Didipio gold and copper mines in South Cotabato and Nueva Vizcaya provinces, where local communities have protested over pollution and water shortages they blame on the mines.
"Since 2017, we could no longer farm on my father's land because it dried up. Many farmlands here no longer function due to irrigation issues," said Myrna Duyan, a member of the Tuwali indigenous group who lives near the Australian-owned open-pit Didipio mine.
Duyan said some Indigenous people had been displaced by the mining, while others said it had split the community between those opposed to the mine and those who saw it as a welcome economic boost.
Despite the perceived economic benefits, "most of the taxes from mining goes to the national government and not to the local communities", said Quirino, whose group says the royalties paid by mining companies should be hiked.
Under current laws, miners pay 4% in excise tax to the state and 1% in royalties to Indigenous communities.
While Philippine President Ferdinand Marcos Jr. has vowed to overhaul the industry's tax regime, the proposed minerals management bill is not among his priority measures and he has not commented publicly on campaigners' wider demands.
The bill, which seeks to raise the current excise tax and royalties to 10% each, also seeks heavier fines on individuals and corporations for human rights and environmental harms.
"If we don't have a framework anticipating the huge demand for minerals, we will only open the country to mining that only promises money but without a nuanced approach to our resources," said Quirino.
(Reporting by Mariejo Ramos. Editing by Amruta Byatnal and Helen Popper. )
Context is powered by the Thomson Reuters Foundation Newsroom.
Our Standards: Thomson Reuters Trust Principles
Tags
- Clean power
- Adaptation
- Fossil fuels
- Indigenous communities