Australia Indigenous referendum hit by 'toxic' disinformation
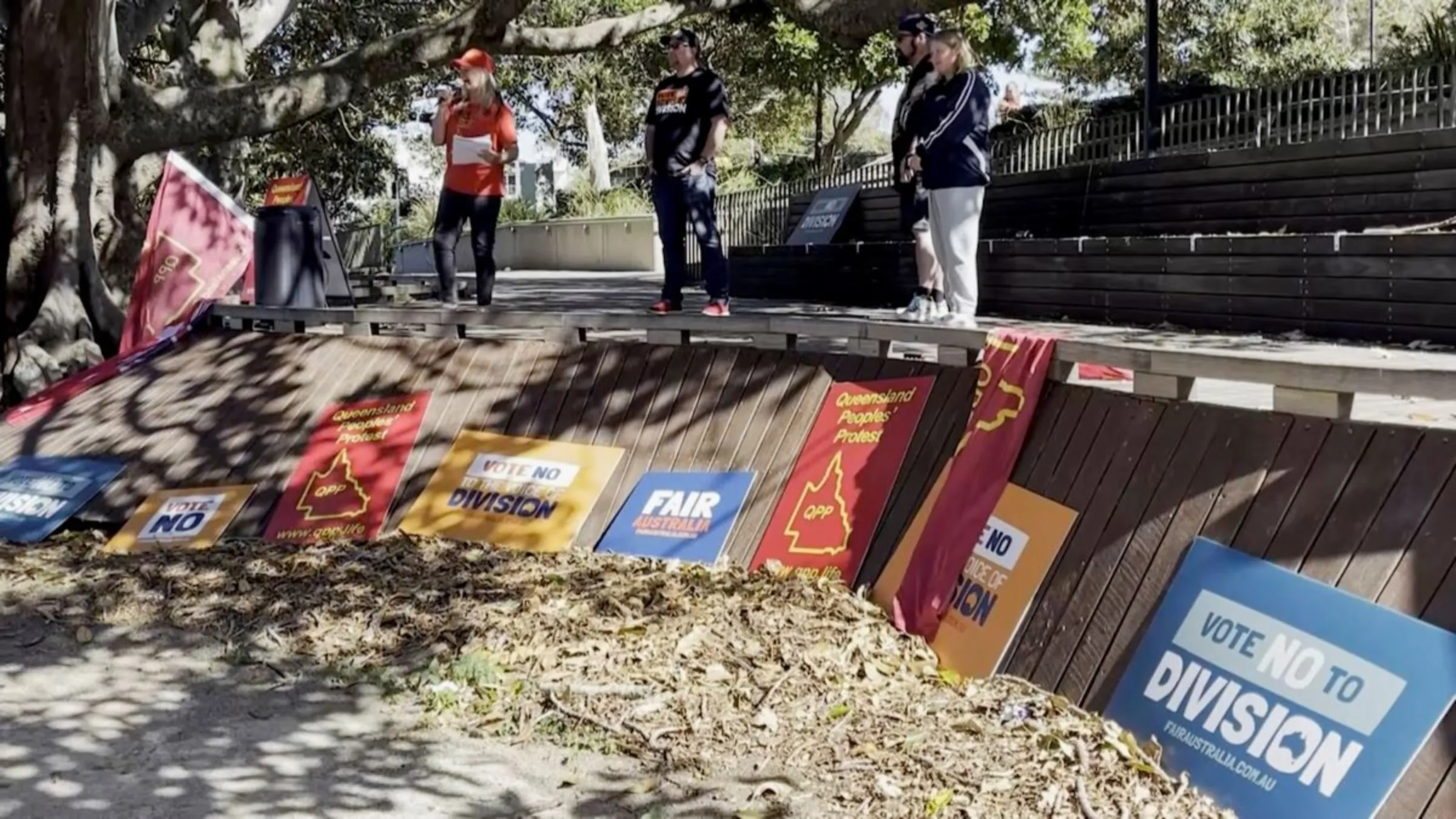

A rally opposing a referendum on whether to establish a constitutionally recognised Indigenous advisory body to parliament in Brisbane, Australia, August 19, 2023, in this screengrab obtained from a video. REUTERS TV via REUTERS
What’s the context?
Ahead of Australia's referendum to recognise Indigenous people in the constitution, disinformation and racist abuse divide voters
- Referendum to recognise Indigenous people in constitution
- Disinformation on social media leads to racist abuse
- Support for referendum has fallen due to disinformation, advocates say
MELBOURNE - In a video that first appeared on Facebook in June, an Aboriginal woman looks intently into the camera as she says Indigenous people will lose their rights over their tribal lands if the upcoming referendum in Australia is in favour of constitutionally recognising Indigenous people.
The more than eight-minute long video quickly went viral, racking up tens of thousands of views and shares across social media platforms even after its claims were debunked.
The video is still on several Facebook pages, with the caveat that it has "partly false information".
It is one of hundreds of videos, tweets and posts spreading disinformation ahead of the Oct. 14 referendum when Australians will be asked if they consent to setting up an Indigenous advisory body to give advice on matters that affect Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people.
AAP FactCheck, a unit of Australian Associated Press, has published more than 90 checks on everything from the rules of the referendum to the false claim that the advisory body, called the Voice to Parliament, would be a private company.
"We have checked claims from both sides, but we have certainly seen more claims from those against the proposal," said Ben James, editor of AAP FactCheck.
"Many are coming from people or groups on social media who have no connection with any of the official campaign groups," he told Context.
Australians are being "systematically misinformed", said Timothy Graham, an associate professor at the Queensland University of Technology who has analysed about 250,000 tweets related to the Indigenous Voice referendum.
Tweets opposing the Voice to Parliament are "characterised by confusion and misinformation about the details of the proposed constitutional amendment and a focus on race and racial division," he said.
"Stoking fear, doubt and uncertainty in audiences puts a major roadblock in their ability to make informed, reasoned choices ... people are divided, confused and fighting each other," he said.
"What we are seeing is information warfare."
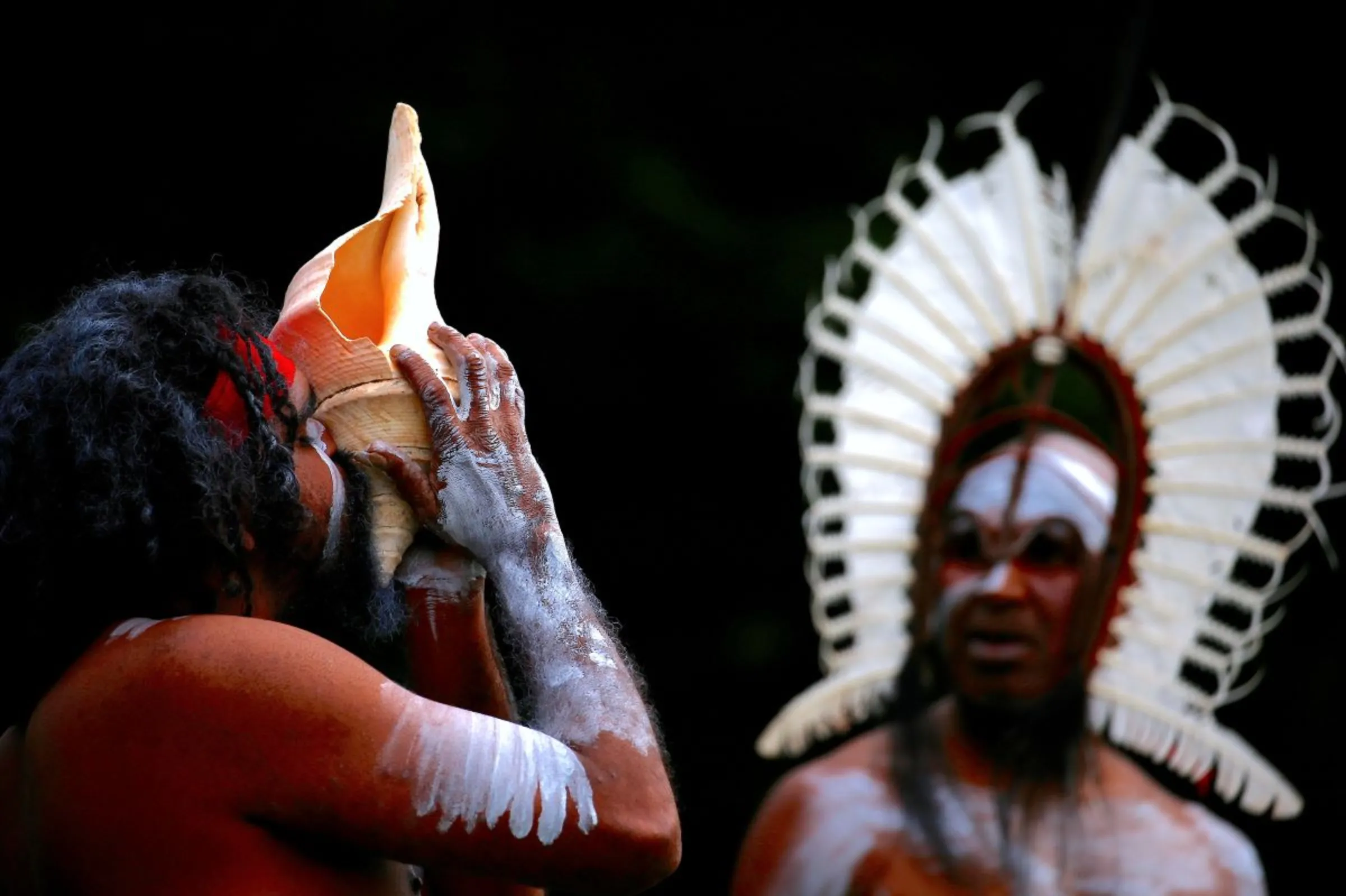

An Australian Aboriginal man blows into a shell as an indigenous man from the Torres Strait Islands wearing traditional dress performs during a welcoming ceremony at Government House in Sydney, Australia, June 28, 2017. REUTERS/David Gray
An Australian Aboriginal man blows into a shell as an indigenous man from the Torres Strait Islands wearing traditional dress performs during a welcoming ceremony at Government House in Sydney, Australia, June 28, 2017. REUTERS/David Gray
'Flood' of disinformation
Australia is a global laggard on relations with its Indigenous people in comparison to many other developed nations including Canada, New Zealand and the United States.
It has no treaty with its more than 800,000 Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people who make up about 3.2% of its population of roughly 26 million and track below its national averages on most socio-economic measures including health.
A call in 2017 for Indigenous people's voice to be enshrined in the constitution was rejected by the conservative government at the time. Last year, the Labor government said it would hold a referendum to include an Indigenous voice to parliament.
"You're being asked to vote for an idea. To say yes to an idea whose time has come," Prime Minister Anthony Albanese said in August while announcing the date of the referendum.
Yet support for the Voice to Parliament has dropped to about 40% from nearly 70% last year, the latest polls show.
The misinformation and disinformation is partly to blame for the fall, say digital rights groups and Indigenous activists, who say they have faced abuse for backing the 'Yes' campaign.
"It has an impact when people believe the lies," said Thomas Mayo, 46, an Indigenous activist who has seen a "massive flood" of disinformation online, and has been a target of racist abuse.
"People believe the disinformation and it makes them angry – and some of them seem to take that out on (us)," he said, adding that much of the disinformation is about non-Indigenous people losing out if the referendum succeeds.
"Things are being said, that you'll lose your backyard or your farm, or that Indigenous people will charge you to use the beach – all that fear-mongering leads to toxicity."
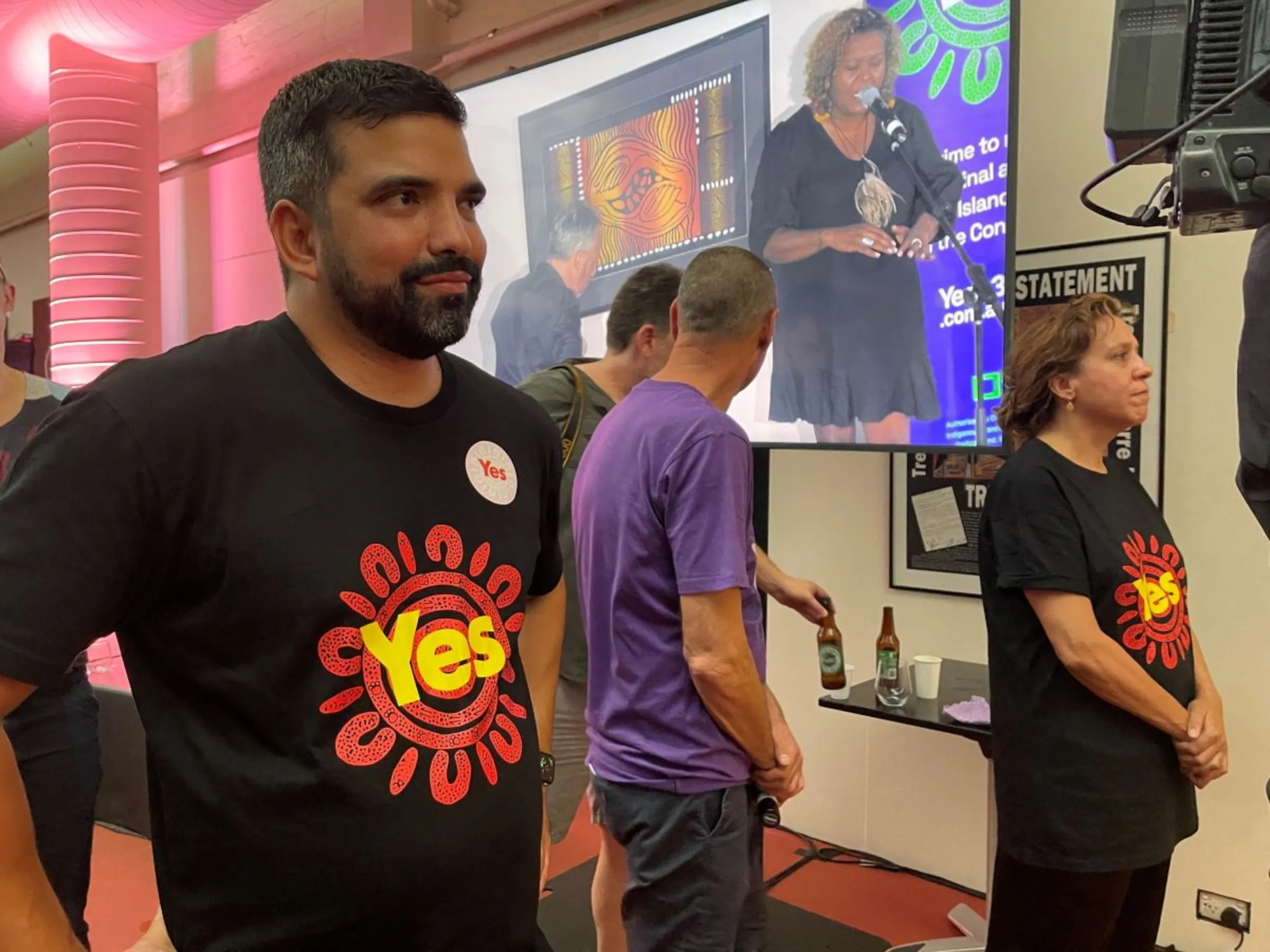

The launch of a campaign for constitutional recognition of Australia's indigenous people, in Adelaide, Australia February 23, 2023. REUTERS/Jill Gralow
The launch of a campaign for constitutional recognition of Australia's indigenous people, in Adelaide, Australia February 23, 2023. REUTERS/Jill Gralow
Racist abuse
Like many other countries, Australia saw an uptick in misinformation during the Covid pandemic and during its federal election last year.
Australia's left-leaning Labor government introduced draft legislation this year that would allow the media regulator to determine what constitutes misinformation, and fine social media firms.
But the bill has been criticised by opposition party members and rights groups, and is not yet law.
Meta - the parent of Facebook, Instagram and WhatsApp - has increased funding for third-party fact-checkers in Australia. But X, formerly known as Twitter, recently removed the ability for people in some countries including Australia to report a tweet for containing misleading information.
The move by X is "badly timed", said internet advocacy group Reset.Tech Australia.
"It is extremely concerning that Australians would lose the ability to report serious misinformation weeks away from a major referendum," it said in an open letter to X last month.
X did not respond to a request for comment.
Much of the disinformation is spread by the 'No' campaign and amplified across social media, said Mary Crooks, executive director at gender rights group the Victorian Women's Trust, and a leader of the 'Yes' campaign.
"Since the referendum campaigns began, there has been a significant spike in racist attacks and abuse even to crisis support lines, and prominent Indigenous 'Yes' campaigners have come in for ugly and pernicious attack on social media," she said.
Jacinta Nampijinpa Price, a conservative senator and 'No' campaigner who is Indigenous, said she had also received racist abuse.
"We have seen ugliness on display from right across the board ... (I) have been the subject of horrible racial vilification," she said at the National Press Club last month.
For referendum supporter Mayo, the antidote to the misinformation and abuse is an open, respectful dialogue and fact-checking of false claims.
"Making sure people are informed is harder, but not impossible," he said.
"When we have conversations with undecided voters and explain that it's a modest reform and no one will lose anything - that tends to cut through the lies quite quickly."
(Reporting by Seb Starcevic and Rina Chandran. Editing by Zoe Tabary)
Context is powered by the Thomson Reuters Foundation Newsroom.
Our Standards: Thomson Reuters Trust Principles
Tags
- Disinformation and misinformation
- Content moderation
- Economic inclusion
- Social media
- Data rights