Respect African content moderators, says Facebook whistleblower
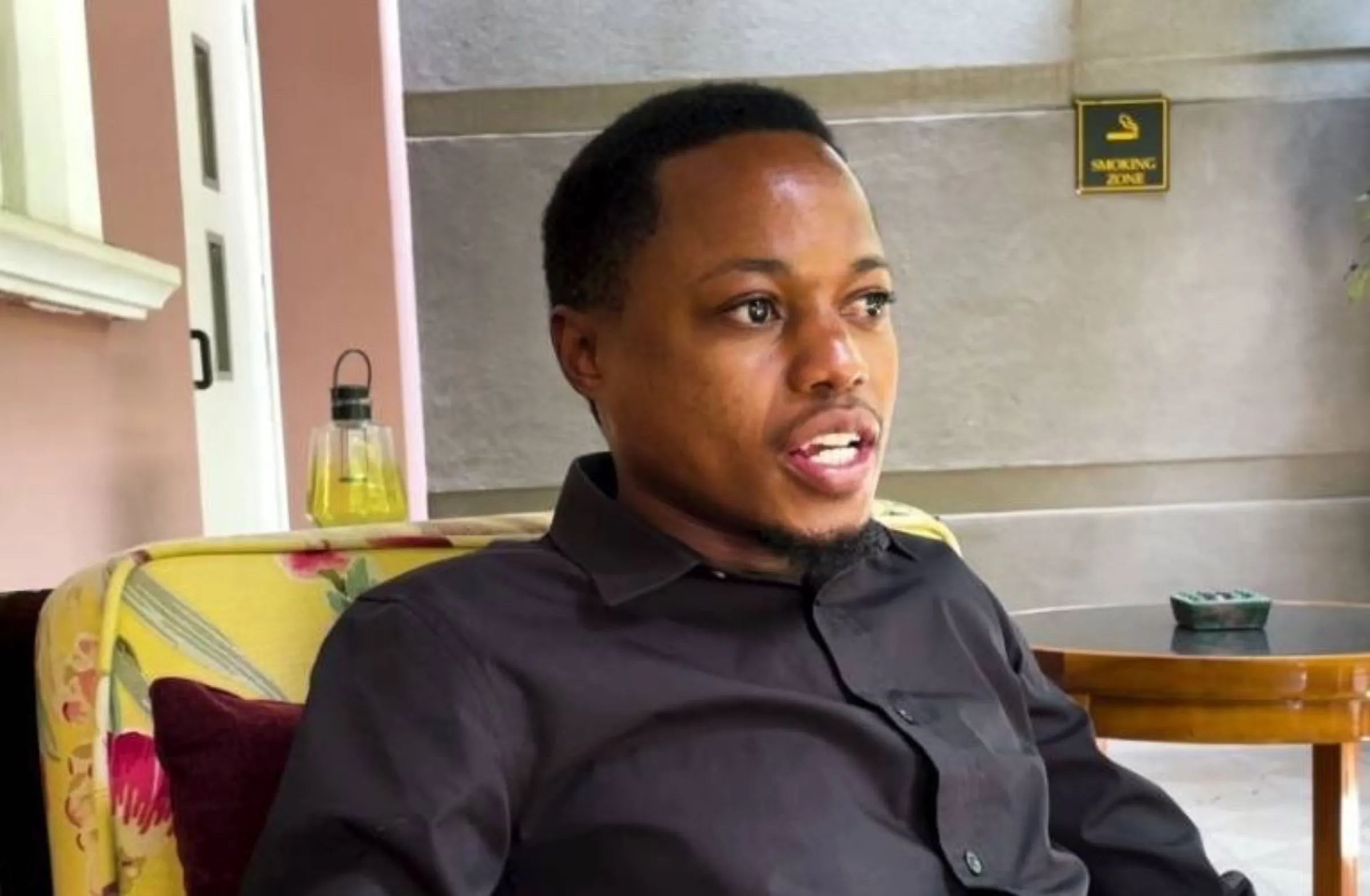

Facebook whistleblower Daniel Motaung in a meeting with his lawyers shortly before his case with Meta was lodged in Nairobi, Kenya, March 2022. Daniel Motaung/Handout via Thomson Reuters Foundation
What’s the context?
Since being fired as a content moderator in Kenya, Daniel Motaung has made it his mission to fight for workers' rights
- Meta faces growing scrutiny over content moderation
- Ex-moderator helps set up union for African workers
- Describes heavy toll of work on mental health
JOHANNESBURG - The first video Daniel Motaung had to watch while working as a Facebook content moderator in Kenya was of a beheading. After just six months in the job, his mental health was spiraling.
"I was actually dysfunctional. I wasn't able to think properly," Motaung, 31, told Context.
Today, he is suing Facebook's owner Meta over the working conditions he faced and has helped set up the first African union for content moderators whose daily job involves reviewing graphic content so social media users are spared from seeing it.
"The entire (social media) business model is actually dependent on content moderation ... It's high time they recognise that and treat us with the respect we deserve," he said following the union's launch last week during a meeting of Facebook, TikTok and ChatGPT moderators in Nairobi.
Globally, thousands of moderators review posts containing graphic content - keeping harmful material from appearing on users' feeds. Many work for third-party contractors rather than directly for tech companies.
Motaung's lawsuit, which was also filed against Meta's local outsourcing company Sama, seeks financial compensation, an order that outsourced moderators have the same healthcare and pay scale as Meta employees, unionisation protection and an independent human rights audit of the office.
Asked to comment on the lawsuit's allegations, a Sama spokesperson said the company cared "deeply about the health and emotional well-being of our team" and disputed accusations of low pay and poor conditions.
A Meta spokesperson said the company does not comment on ongoing litigation but only works with contractors that ensure above-average pay and well-being support.
As Meta faces growing scrutiny over its content moderation, Motaung's lawsuit could have implications for how the firm works with moderators worldwide, said Cori Crider, a director at Foxglove, a London-based tech-justice advocacy group supporting the case.
"That's the ambition of this case: to force Facebook to honour moderation work and make it safe and fair," she said in emailed comments.
'Flashbackas and insomnia'
Motaung, who is South African, said he did not expect his university studies on workers' rights to come in handy when he accepted the content moderation job in Nairobi in 2019, but soon felt impelled to speak up about the conditions.
He recounted seeing colleagues fainting, crying and binge-drinking and hearing others complain of flashbacks and insomnia.
Most of Sama's moderators were paid less than $2 per hour, but many stuck with the job because they were made to feel "expendable" and desperately needed the work, Motaung said.
The Sama spokesperson detailed well-being policies including mandatory work breaks, limits on weekly hours and counselling sessions, and said wages were high in local terms.
"We recognize that content moderation is a tough job and have paid wages that are four-times the minimum wage and 2.5-times the living wage in Kenya as a recognition of the challenges of that work," the spokesperson said in an email.
Motaung, who was fired by Sama when he banded together with fellow moderators to challenge working conditions, said he now saw his main job as speaking out about "the politics of content moderation".
His activism has spurred further legal action from content moderators and global support from rights groups. In March, 43 applicants said they are also suing Meta for losing their jobs after organising a union.
His lawsuit is also seen as significant because a labour court ruled that the U.S.-based company could be sued in the East African country - a judgment that Meta swiftly appealed.
"At the core of the case is a fundamental question: can the world's richest tech firms operate in Kenya, and profit from workers in Kenya, while refusing to answer to Kenyan justice?" Crider said.
"The answer to this question will set the terms of tech accountability in the region for years to come," she said.
Motaung, who was eventually diagnosed with post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), urged other content moderators to speak up for their rights.
"There are support systems, there are organisations out there ... that can help," he said.
"Or find me, send me a message ... don't die in silence," he said.
(Reporting by Kim Harrisberg; Editing by Helen Popper.)
Context is powered by the Thomson Reuters Foundation Newsroom.
Our Standards: Thomson Reuters Trust Principles
Tags
- Content moderation
- Facebook
- Tech regulation
- Meta
- Social media