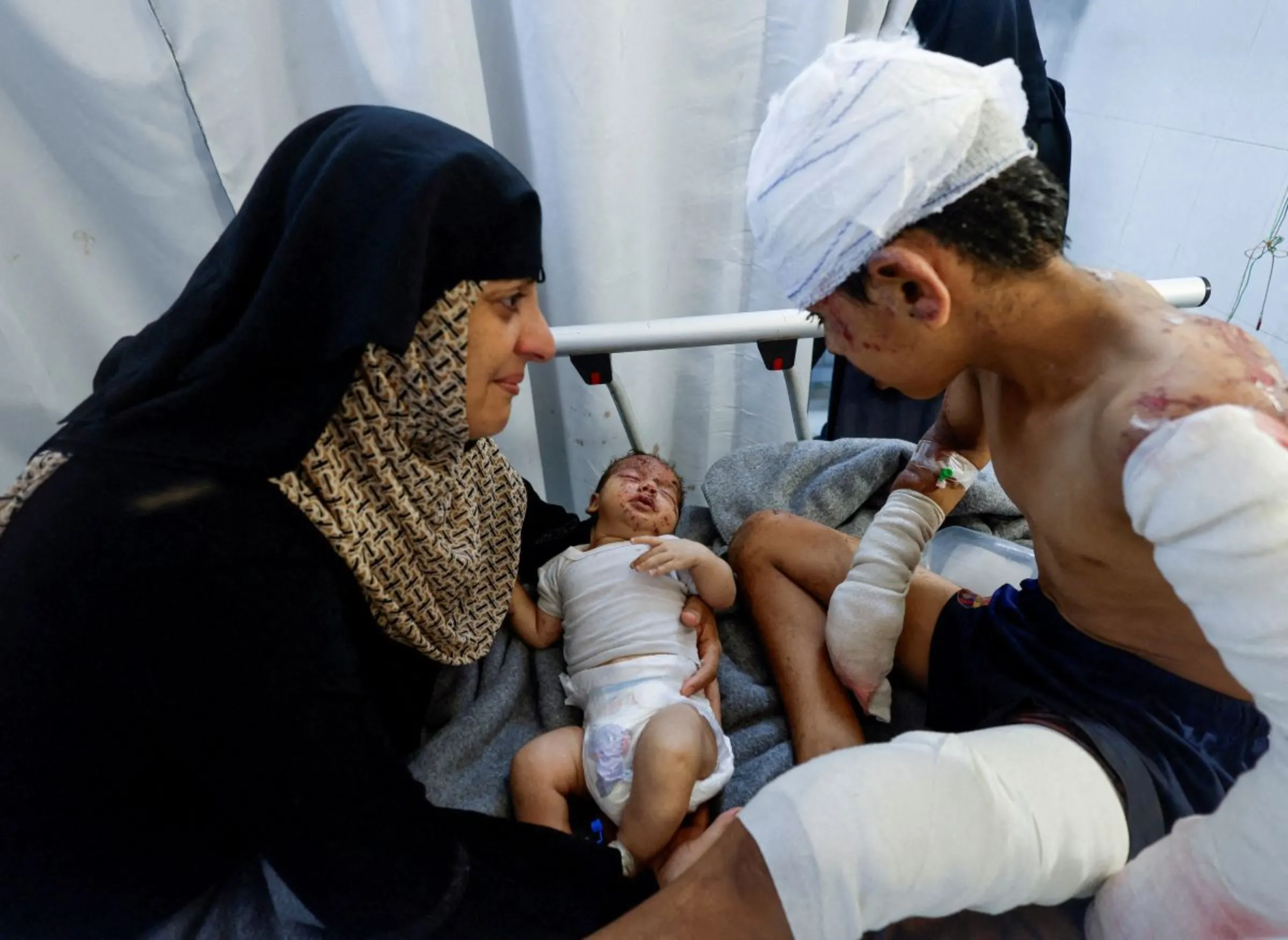
Gaza's pregnant women defy odds to give birth, protect babies
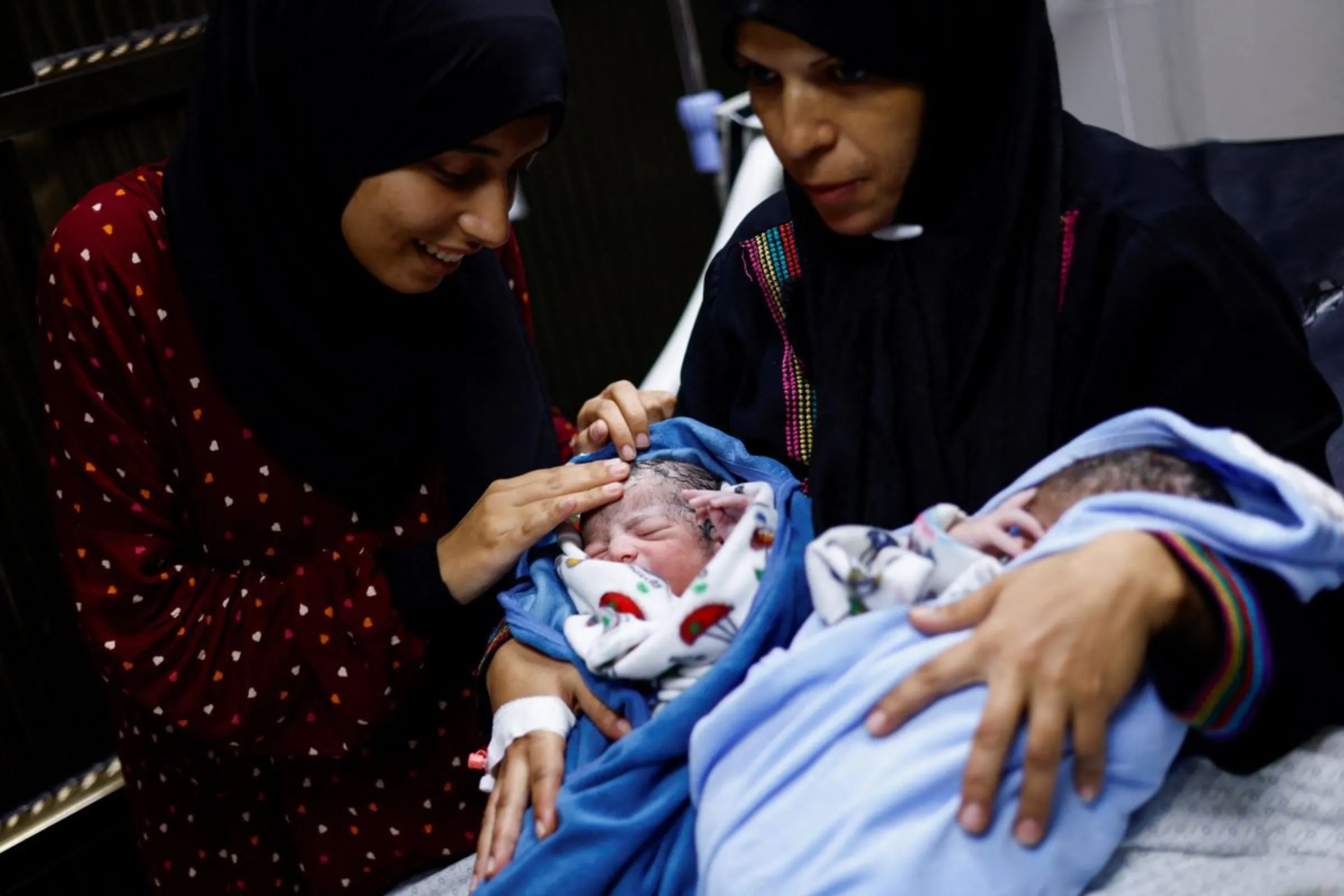
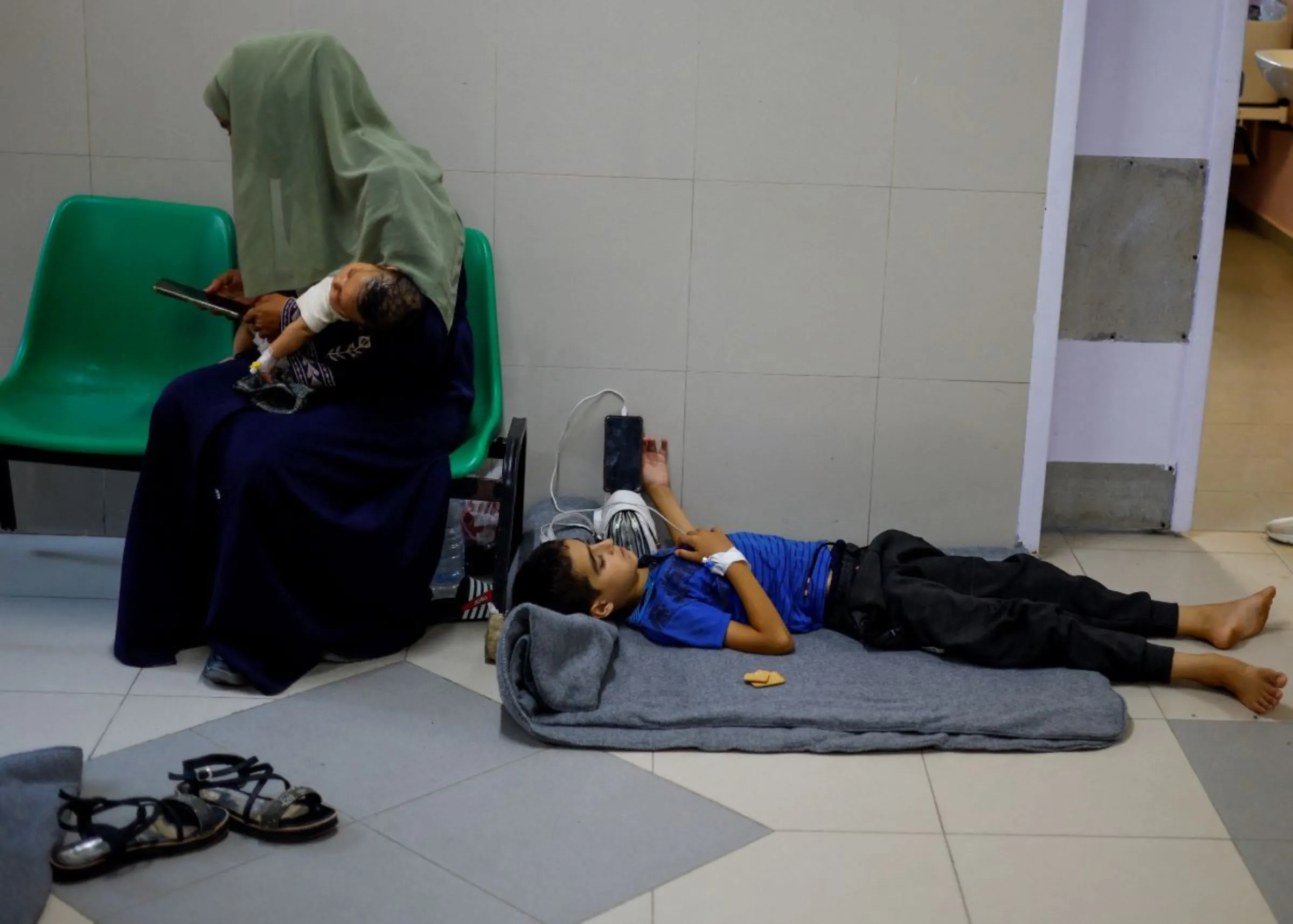
A Palestinian woman holds her newborn twins at Nasser hospital, in Khan Younis in the southern Gaza Strip, Nov. 2, 2023. REUTERS/Mohammed Salem
What’s the context?
In Gaza, Palestinian women give birth in crowded hospitals or tents but that's just the start of a battle to protect their babies
- Pregnant women struggle to get to overcrowded hospitals
- Repeated displacement makes medical care almost impossible
- New mothers forced to improvise solutions
BEIRUT - In a flimsy tent crouched low among the smashed buildings of Rafah, Palestine Bahr felt her contractions begin early one day in May. Her baby was coming but how would she make her way through the rubble-strewn streets to hospital without a car?
She managed to find a donkey cart and rattled her way through the streets of the city in southern Gaza as her contractions got stronger.
When she arrived at the Al Helal Al Emirati Maternity Hospital, she was tenth in line and had to wait for three hours before even getting to see a doctor. It was another three hours before she was taken into an operating room where she gave birth to a daughter, Ghina, by Caesarean.
But then Bahr developed blood clots. With no beds available for in-patients, she went back to her tent, resigning herself to travelling to and from the hospital for treatment.
Then, two days after giving birth, she was forced to flee her makeshift home when Israeli forces stormed Rafah. It was the fourth time Bahr, who is originally from the central city of Deir al-Balah, had to flee because of the conflict.
"Since the war began, it has been a constant fight for survival, even for the most basic human right: bringing a child safely into the world," Bahr, 33, told Context in a phone interview from Khan Younis in late May.
"It wasn't just the physical pain, but the constant worry gnawing at me – would my baby be okay? Would I be okay?"
Bahr is among thousands of women who have run the gauntlet of bombs and bullets to bring life into a land where more than 38,000 people have been killed by the Israeli military since its war with Hamas militants in the Gaza Strip began nine months ago, according to the Palestinian health ministry.
The offensive came after Hamas-led militants stormed into Israel on Oct. 7, killing around 1,200 people and taking 250 hostage, according to Israeli figures.
Since then, over half of Gaza's 2.3 million people have crowded into Rafah, seeking shelter from an offensive that has laid waste to homes, schools and vital infrastructure such as hospitals and clinics.
More than 87,000 people have been wounded and the few hospitals that are still functioning struggle to cope with the daily influx of people injured in Israeli airstrikes.
In May, the World Health Organization said only about one-third of Gaza's 36 hospitals and primary health care centres were still partially operational.
Israel justifies attacks on hospitals by saying that Hamas uses them for military purposes - a claim both hospital staff and Hamas deny.
For new mothers like Bahr, giving birth in a warzone is just the first step on a traumatic journey marked by constant fear and anxiety.
"The makeshift tent barely shields us from hot weather or bad weather, let alone the constant fear that grips our hearts. It's no place to raise children, no place to recover from childbirth," Bahr said.
"My body is barely healed from childbirth, and now I have to fight to keep my daughter alive."
'Born into hell'
The U.N. children's agency UNICEF has said that mothers in Gaza face "unimaginable challenges" in accessing adequate medical care, nutrition, and protection before, during and after giving birth.
"The trauma of war also directly impacts newborns, resulting in higher rates of undernutrition, developmental issues and other health complications," Tess Ingram, UNICEF's communications specialist, said during a press conference in Geneva in January.
"Becoming a mother should be a time for celebration. In Gaza, it's another child delivered into hell," Ingram said.
In May, the main maternity hospital in Rafah, where Bahr gave birth, stopped admitting patients.
The hospital has seen a drop of over 50% in staff and patients since Israeli forces entered Rafah in May, said Naheel Jarrour, an obstetrician who works at the hospital.
"We had prepared places for pregnant women on the floor to get treatment or even to deliver their babies because there were not enough beds for them," she said, adding that the fighting had prevented her from getting to the hospital for weeks.
Aurélie Godard, head of Médecins Sans Frontières' (Doctors Without Borders) medical activities in Gaza, said many women are being forced to give birth outside the formal medical system.
"It is still a challenge for many women especially in Rafah to have access to transportation and to hospitals," Godard told Context.
Despite their efforts, humanitarian organisations have been finding it difficult to provide services to around 2,200 women who give birth in Gaza every month, she added.
"My friend was trapped in the north and had to deliver her baby at home," Jarrour said. "Alone in the bathroom, she cut the umbilical cord herself with scissors."
There has also been a rise in miscarriages because of the lack of food and stress of constant danger and displacement, according to ActionAid.
Godard said patients who were critically ill and in intensive care were also being placed at risk by evacuation orders that meant medical equipment had to be moved around constantly.
Other hospitals in Rafah, such as Abu Yousef al-Najjar hospital and the Kuwaiti hospital, have been forced to close due to evacuation orders.
Hungry babies
The trauma for new mothers continues after birth as they try to care for their babies with food, power and other essential supplies in short supply.
More than 495,000 people across the Gaza Strip are facing the most severe, or "catastrophic", level of food insecurity, according to an update from the Integrated Food Security Phase Classification (IPC), an initiative of U.N. agencies, regional bodies and aid groups.
Israel says it puts no limit on humanitarian supplies for civilians in Gaza and has blamed the United Nations for slow deliveries, saying its operations are inefficient.
Medicines are in short supply, forcing new mothers to improvise as they care for their babies.
"The fear is constant. Will this homemade remedy work? Will I make things worse? This isn't the kind of fear a mother should have to live with," said 23-year-old Asmaa Salah Abu Jabal in an interview with Context.
She was forced to turn to the internet to try to find alternatives to treat her four-month-old daughter's cold.
"We cannot be doctors overnight, desperately searching the internet for answers," she said.
Soad Al Masri, a 19-year-old who recently gave birth, described the challenges of caring for her newborn daughter Layan in a tent made unbearable by the scorching summer heat.
"My daughter feels suffocated in her winter clothes that we borrowed from neighbours," she said. "It is extremely hot and there is no air."
In search of some relief, Masri often walks her daughter down to the seashore, hoping for a cool breeze.
"Every time the sight of my daughter struggling to breathe takes my soul."
(Reporting by Menna Farouk; Editing by Clar Ni Chonghaile.)
Context is powered by the Thomson Reuters Foundation Newsroom.
Our Standards: Thomson Reuters Trust Principles
Tags
- Gender equity
- War and conflict